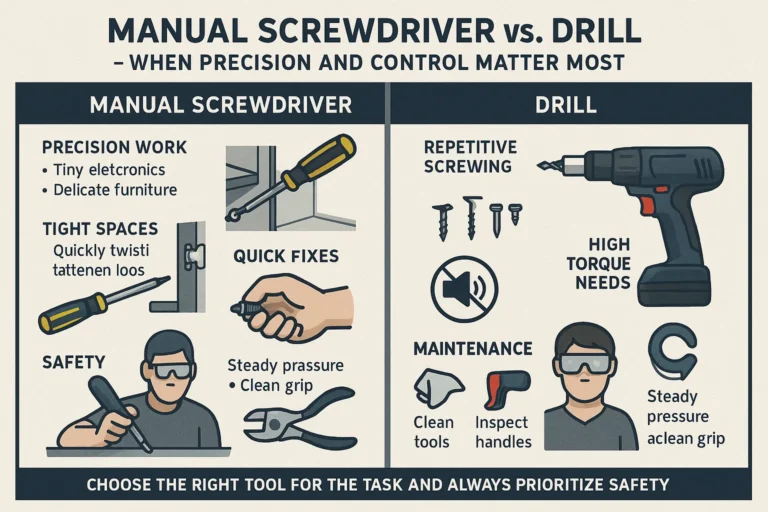
Is transitioning to all-electric home with power tools worth it environmentally?

The Right Order to Transition to an Electric Home
Conducting an energy audit is the crucial first step in transitioning to an electric home. This process assesses your current energy consumption and identifies opportunities for efficiency improvements. It often reveals how much energy specific appliances waste, helping you prioritize replacements and upgrades that will yield the most significant savings over time. Moreover, an audit facilitates a comprehensive approach to electrical work—upgrading your electrical systems in one go minimizes disruption and ensures that your home can safely support new appliances.
When upgrading, it’s advisable to replace appliances as they age. Older appliances typically consume more energy, which can negate the benefits of switching to electric sources. Modern electric appliances are designed for energy efficiency, often using considerably less power than their older counterparts. By replacing outdated equipment, you not only enhance your home’s energy efficiency but also reduce overall energy costs significantly over the long term. For instance, Energy Star-rated appliances can use 10-50% less energy and water than standard models, thereby promoting sustainability while saving money on utility bills.
Making these transitions not only decreases reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a lower carbon footprint, supporting global efforts towards a cleaner environment. Consequently, transitioning to an electric home is not merely a practical decision—it’s a step towards a more sustainable future.
Preparing an Old House for Electrification
To assess whether an old house is suitable for electrification, several factors must be considered:
- Electrical System Condition: Evaluate the existing electrical wiring and infrastructure. Most older homes may not support modern electrical demands and could require rewiring or upgrading the electrical panel to accommodate new appliances. It’s essential to check for safety issues, such as outdated insulation and circuit breakers that may need replacement.
- Appliance Replacements: When transitioning to electrification, it’s crucial to identify which appliances need to be replaced. Older appliances often do not meet energy efficiency standards and can be a potential fire hazard. Look for energy-efficient models that comply with current regulations, prioritizing items like stoves, heaters, and water heaters that can significantly impact overall energy consumption.
- Structural Improvements: Structural adaptations may be necessary to facilitate electrification. This may include enhancing insulation to reduce energy consumption, installing modern circuit systems that distribute energy efficiently, and ensuring that the existing electrical infrastructure can handle the load of new appliances. Upgrading outlets and switches is also advisable to meet safety standards.
- Compliance and Regulations: Ensure that any electrification plans comply with local building codes and electrical regulations. It may be necessary to consult with professionals or local authorities to get the right permits and inspections before starting the electrification process.
For further information on electrical safety and home improvement projects, consider exploring articles on home improvement projects and power tool safety tips.
Equipment Considerations for Home Electrification
Electrification upgrades require careful assessment of essential equipment and outlet requirements. Key devices often involved in this process include electrical panels, circuit breakers, wiring, and outlets.
- Electrical Panels: Upgrading or installing a new electrical panel is crucial to handle additional power loads efficiently. Many modern homes require panels rated at 200 amps to support current electrical demands, especially with the prevalence of high-power appliances and electronic devices. It’s advisable to consult the National Electrical Code (NEC) for guidelines on panel specifications and requirements.
- Circuit Breakers: Adequate circuit breakers are essential not only for safety but also for accommodating future upgrades. A system that includes breakers rated for specific circuits (like 20 or 30 amps) aligned with appliance needs helps prevent overload situations.
- Wiring: The condition and type of wiring within your home will greatly influence the feasibility of electrification upgrades. Homes wired with outdated materials like aluminum may require re-wiring to enhance safety and performance. Upgrading to copper wiring is recommended for better conductivity.
- Outlets and Receptacles: Assessing and upgrading existing outlets is vital for compatibility with modern devices. GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets are necessary in wet areas to ensure safety, while standard outlets may need to be upgraded to accommodate higher-voltage devices. The NEC requires specific outlets for appliances over a certain wattage, making it essential to evaluate your current setup.
- Surge Protectors and Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): For sensitive equipment, incorporating surge protectors can provide protection from voltage spikes. A UPS is also beneficial, ensuring devices like computers maintain power during outages.
For detailed projects and best practices concerning power tools and their required upgrades, consider reviewing articles on the specifics of project management and equipment choices.
Sources
- U.S. Department of Energy – Energy Audits
- U.S. Department of Energy – Energy Star-rated Products
- National Fire Protection Association – Codes and Standards
- One Power Tool – Home Improvement Projects
- One Power Tool – Features of a Good Electric Hand Drill
- One Power Tool – Power Tool Usage Projects
- One Power Tool – Best Practices for Power Tools